Cogeneration
Cogeneration, also known as Combined Heat and Power (CHP), is the simultaneous production of electricity and useful heat. Compared to conventional power generation systems where electricity and heat are produced from separate sources, CHP systems increase energy security by producing energy at the point of use and significantly improve energy efficiency.
CHP systems offer economical, environmental, and reliability-related advantages. Additional benefits for the industry like increased reliability, power quality, and higher productivity.
Economic benefits:
The costs for the cogeneration (CHP) system projected out over the expected life of the equipment are far lower for CHP systems than where a facility continues to purchase all its electricity from the grid and gas for heating. The lifetime costs of the CHP include the equipment and installation, the operation & maintenance, and the energy costs.
Energy benefits:
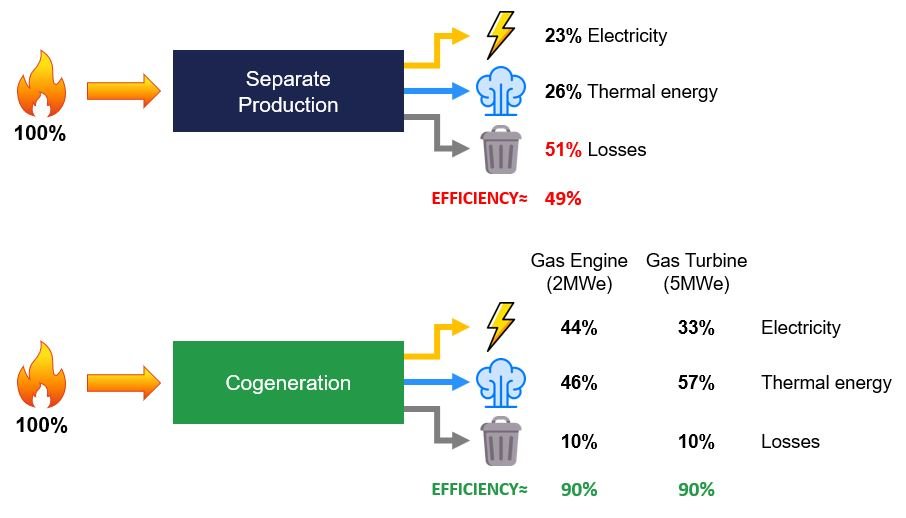
A typical cogeneration (CHP) system can reduce energy requirements by around 40 percent compared to separate heat and power production.
Environmental benefits:
By increasing energy efficiency, which can reach up to 90%, CHP significantly reduces the emissions footprint of pollutants such as NOx and SO2, and other greenhouse gases such as CO2.
Other benefits:
In some countries, cogeneration (CHP) and other on-site generation options can offer grid support to the local distribution utility, including:
- Voltage and frequency support to enhance reliability and power quality
- Avoidance or deferral of high-cost, long lead time T&D upgrades
- Bulk power risk management
- Reduced line losses, reactive power control
- Outage cost savings
- Reduced central station generating reserve requirements
- Transmission capacity release
